Unlocking Road Safety: The Impact of European Regulation UN ECE R151
Unlocking Road Safety: The Impact of European Regulation UN ECE R151
In the ever-evolving landscape of road safety, technological advancements have emerged as a beacon of hope. One area where these innovations shine is in the realm of blind-spot monitoring systems. When it comes to heavy vehicles like trucks and buses, the challenge of blind spots becomes even more critical. That’s where European Regulation UN ECE R151 comes into play, revolutionizing road safety for drivers and vulnerable road users like cyclists. This regulation aims to harness cutting-edge technology to erase blind spots and enhance road safety.
The Genesis of European Regulation UN ECE R151
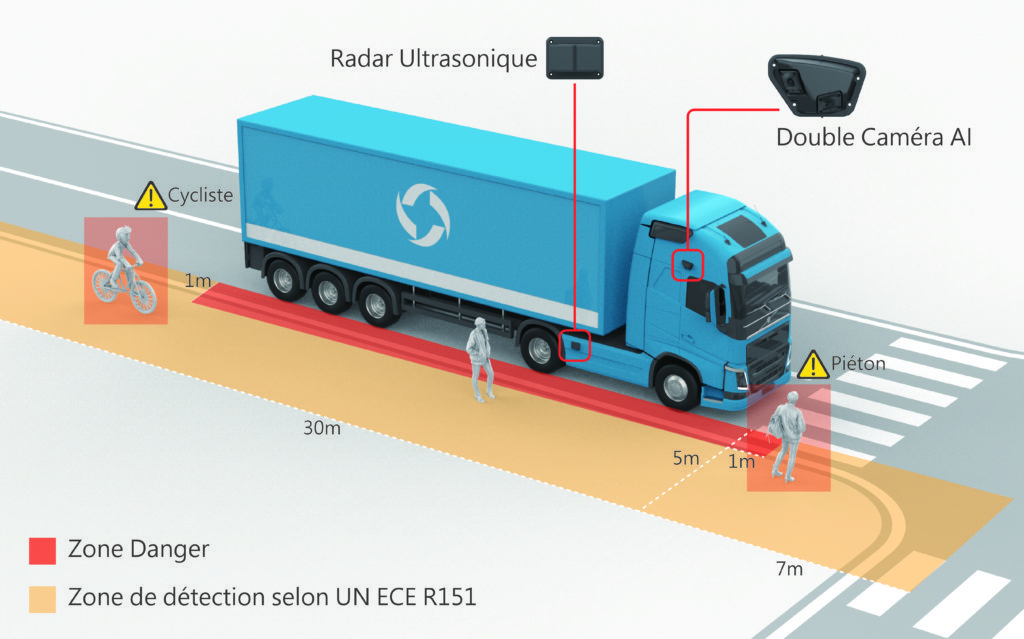
The genesis of this regulation lies in the undeniable fact that larger vehicles often grapple with blind spots, leading to potentially hazardous situations involving cyclists. European Regulation UN ECE R151, known as the Blind Spot Information System (BSIS) for the Detection of Bicyclists, was introduced to elevate the safety standards for drivers of heavy vehicles, particularly during complex maneuvers. While the addition of extra mirrors has undoubtedly contributed to reducing collisions, this regulation seeks to leverage the latest technological advancements to eradicate blind spots.
Key Highlights of the Regulation
The crux of the regulation revolves around empowering drivers with early notifications when a bicycle might enter a critical zone, thus preventing potential accidents. Additionally, it mandates a secondary signal when a collision becomes imminent, acting as a last line of defense.
The BSIS doesn’t stop there. It also plays a pivotal role in alerting the driver when a cyclist could be endangered during a large vehicle’s turn, allowing the driver to take corrective action promptly. Signals are designed to escalate in frequency as the risk of a collision intensifies.
To ensure drivers aren’t bombarded with false alarms, the BSIS possesses the capability to distinguish between vulnerable objects like cyclists and non-vulnerable objects such as street furniture, traffic signs, and parked cars, while still issuing a warning when a genuine collision risk arises.
Vehicle Categories Affected by R151
European Regulation UN ECE R151 casts its safety net over specific vehicle categories:
- M2
- M3
- N2
- N3
- Vehicles designed for passenger transport with more than eight seats (excluding the driver’s seat) and a maximum mass that doesn’t exceed five tonnes.
In a nutshell, European Regulation UN ECE R151 is a pivotal stride towards eradicating blind spots in heavy vehicles, safeguarding vulnerable road users, and promoting road safety. As we continue down the road of progress, regulations like R151 pave the way for safer journeys for all.